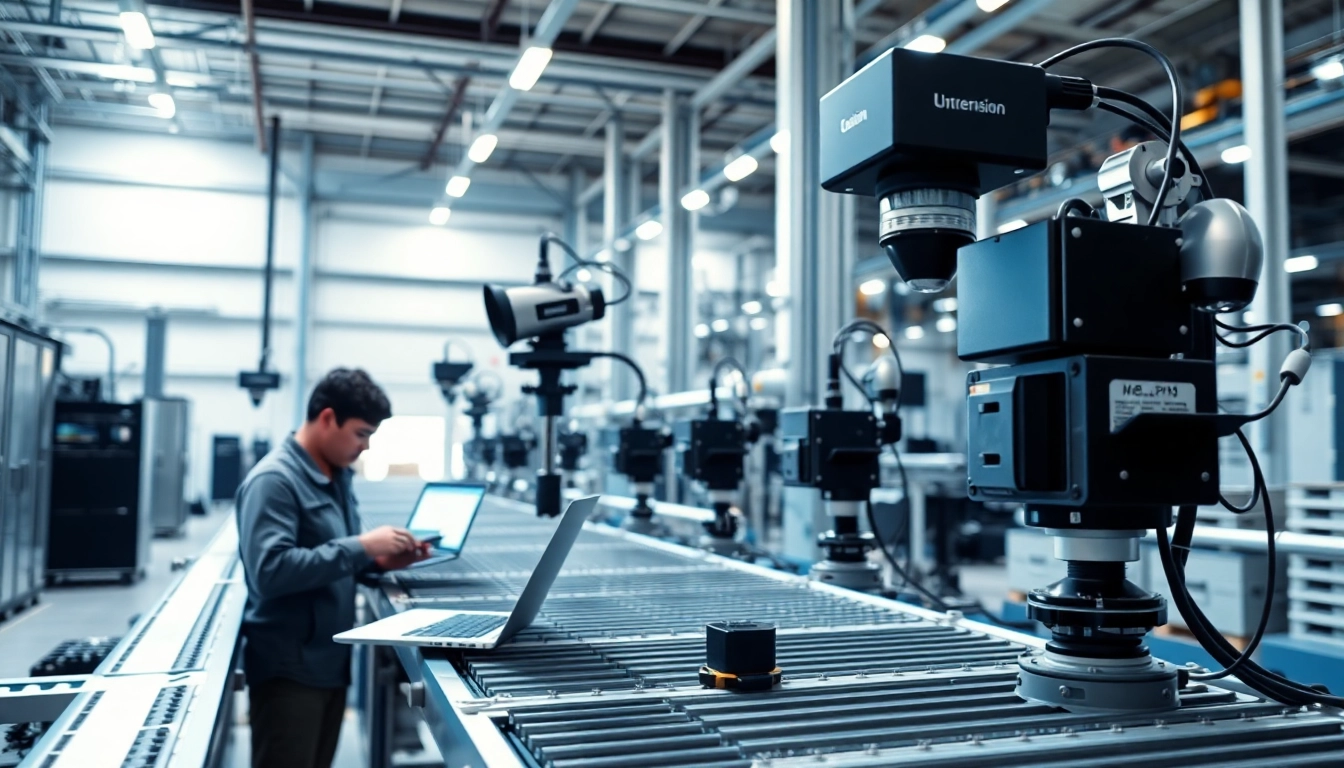
What is Machine Vision?
Machine vision is an advanced technology that uses imaging-based techniques to automate the inspection and analysis of objects in various industries. By employing sophisticated camera systems and processing algorithms, machine vision enables machines to interpret visual information similarly to humans. As industrial automation and quality control mechanisms evolve, machine vision continues to gain prominence in diverse applications from manufacturing to healthcare. For those interested in exploring this technology further, a detailed overview can be found at machine vision.
Definition and Core Concepts
Machine vision encompasses a range of technologies that allow a system to “see” and process images, translating the visual input into actionable insights. At its core, machine vision aims to replicate human visual perception through electronic means. This involves capturing images using cameras, processing them through hardware and software, and making decisions based on analyzed information.
How Machine Vision Works
The operation of machine vision systems involves several key stages:
- Image Acquisition: The initial stage involves capturing an image using a camera. Depending on the application, specialized optics may be employed for high precision.
- Image Processing: Once the image is acquired, software algorithms process it to identify patterns, features, or defects. This can include techniques like edge detection, filtering, and pattern recognition.
- Analysis: The processed images are analyzed according to predefined criteria. This enables systems to make informed decisions, such as identifying faulty products on a production line.
- Output: The final step involves outputting the results, whether that be in the form of alerts, quality reports, or automated adjustments to machinery based on vision feedback.
Key Components of Machine Vision Systems
Successful machine vision systems typically consist of several integral components:
- Cameras: High-resolution cameras designed specifically for industrial applications capture images under various lighting conditions.
- Illumination: Proper lighting is essential for optimal image capture. Various illumination methods, such as LED and laser lighting, are used depending on the specific requirements of the application.
- Processing Hardware: Dedicated processing units or computers are used to handle complex image processing tasks, ensuring rapid analysis and response time.
- Software Algorithms: Advanced algorithms are vital for interpreting the visual data correctly. These may be programmed for specific tasks, like identifying irregularities in products or reading barcodes.
- Connectivity Infrastructure: Machine vision systems often require a network to communicate with other machines and systems, ensuring seamless integration within manufacturing or operational workflows.
Applications of Machine Vision
Machine vision technology finds applications across various sectors, each leveraging its ability to enhance efficiency and accuracy in processing visual data.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
In manufacturing, machine vision plays a pivotal role in quality control. It is instrumental in inspecting products in real-time for defects, ensuring that only items meeting quality standards proceed through the production line. Key applications include:
- Defect Detection: Automated systems can quickly identify scratches, dents, or color mismatches that might be missed by the human eye.
- Assembly Verification: Machine vision systems verify whether components are properly assembled, reducing errors and rework.
- Barcode and QR Code Reading: These systems can swiftly read barcodes and QR codes for inventory management and tracking, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Healthcare Imaging
In healthcare, the implications of machine vision are profound. Imaging systems that utilize machine vision technology assist in diagnostics and treatment. Examples include:
- Medical Imaging: High-resolution imaging systems are used for radiology, allowing for detailed analysis of x-rays and MRIs.
- Pathology: Automated systems can analyze biopsy samples to detect abnormalities or cancerous cells with higher accuracy than manual methods.
- Robotic Surgery: Machine vision enhances robotic systems in surgical procedures, allowing greater precision and reduced recovery times for patients.
Robotics and Automation
Robots equipped with machine vision capabilities enhance their functional capabilities, enabling them to perform complex tasks in dynamic environments. This application is prevalent in logistic operations and manufacturing:
- Vision-guided Robotics: Robots can navigate environments and perform tasks like picking and placing items with higher efficiency, reducing downtime and human error.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Machine vision plays a critical role in allowing self-driving cars to understand and interpret road conditions, enhancing safety and navigation.
- Drone Technology: Drones utilize machine vision for tasks such as surveying land, monitoring crops, or delivering medical supplies in hard-to-reach areas.
Benefits of Implementing Machine Vision
The implementation of machine vision systems offers numerous advantages that lead to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness across industries.
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
One of the foremost benefits of machine vision is the heightened accuracy it provides in visual inspections. Unlike human inspectors, machines do not experience fatigue, ensuring consistent performance over extended periods. Automated systems significantly reduce error rates, leading to higher product quality and fewer returns or complaints.
Reduction of Labor Costs
By automating tasks traditionally performed by human workers, companies can achieve significant reductions in labor costs. Machine vision systems streamline processes, reduce the need for extensive manual inspections, and allow human resources to be allocated to more complex and strategic roles.
Real-time Data Processing
Machine vision systems provide real-time data processing capabilities, enabling immediate feedback and response to anomalies in production or operational processes. This real-time feedback loop can lead to faster adjustments in manufacturing, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous operations.
Challenges in Machine Vision
Despite its benefits, implementing machine vision systems also presents various challenges.
Integration with Existing Systems
One significant challenge is integrating new machine vision systems with existing operations. Companies may face compatibility issues with legacy systems or require adjustments to their workflows to fully benefit from automated visual inspection.
High Initial Investment
Moreover, the initial investment required for machine vision technology can be substantial. Costs associated with purchasing hardware, installing systems, and training personnel can deter some organizations from moving forward with implementation.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
With the gathering and processing of visual data, concerns regarding data security and privacy arise. Organizations must ensure robust cybersecurity measures are in place to protect sensitive information collected via machine vision systems, particularly in applications related to healthcare or personal data.
Future Trends in Machine Vision Technology
The landscape of machine vision technology is continually evolving. Future trends indicate advancements that will further deepen its integration into industry.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into machine vision systems is set to revolutionize the sector. By leveraging AI, systems can learn from previous inspections, enabling them to improve their accuracy and expand their application scope over time.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
Emerging advancements in sensor technology will likely enhance the capabilities of machine vision systems. New sensors can provide higher accuracy and resolution, leading to more detailed image analyses and superior performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Potential Industry Disruptions
Machine vision is poised to disrupt various industries by enabling smarter and more efficient practices. The growing trend towards automation across sectors like agriculture, logistics, and even retail suggests that machine vision will increasingly support innovations that transform traditional processes into more agile and data-driven operations.